2017 IPPF/Standards
This page refers to the 2017 IPPF/Standards |
Click here for the 2024 IPPF/Global Internal Audit Standards |
Internal auditors don't just follow rules, we have standards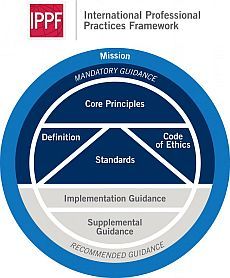
The mission for internal auditing is to enhance and protect organisational value by providing risk-based and objective assurance, advice and insight.
We rely on a framework of principles and standards to help us achieve this – the International Professional Practices Framework.
Mission
To enhance and protect organizational value by providing risk-based and objective assurance, advice and insight.
The Mission Statement to the IPPF provides a clear and succinct description of what internal audit aspires to achieve within organizations. Like a typical mission statement, the Mission of Internal Auditing describes internal audit’s primary purpose and overarching goal.
Achievement of the mission is supported by the entire IPPF: the Core Principles, the Definition, the Code of Ethics, the Standards, and all guidance.
Mandatory guidance
Some elements of the IPPF are considered essential to the professional practice of internal auditing – they are mandatory for members of the Chartered IIA. Members agree to conform to these principles with they join the institute. The mandatory elements of the IPPF, which are explored in more depth below, are:
Definition of internal auditing
Core principles
Code of ethics
International Standards
1. Definition of internal auditing
Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organisation's operations. It helps an organisation accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes.
2. Core principles
The Core Principles, taken as a whole articulate internal audit effectiveness. For an internal audit function to be considered effective, all Principles must be present and operating effectively.
How an internal auditor, as well as an internal audit function, demonstrates achievement of the Core Principles may be quite different from organisation-to-organisation but, failure to achieve any of the Principles implies that an internal audit activity is not as effective as it could be in achieving internal audit’s mission.
- Demonstrates integrity.
- Demonstrates competence and due professional care.
- Is objective and free from undue influence (independent).
- Aligns with the strategies, objectives, and risks of the organisation.
- Is appropriately positioned and adequately resourced.
- Demonstrates quality and continuous improvement.
- Communicates effectively.
- Provides risk-based assurance.
- Is insightful, proactive, and future-focused.
- Promotes organisational improvement.
The Demonstrating the Core Principles for the Professional Practice of Internal Auditing: Enablers and Key Indicators guide explains the concepts embodies in the Core Principles and describes enablers, or specific ways to enable and demonstrate them. The guide also identifies measurable key indicators that enable the internal audit activity to define, measure, assess, and monitor demonstration of the Core Principles. Read the guide here
3. Code of ethics
The internal audit profession is founded on the trust placed in its objective assurance about risk management, control, and governance. The code of ethics provides principles and rules of conduct relating to integrity, objectivity, confidentiality and competency.
Read more about the code of ethics
4. International Standards
The International Standards is an authoritative set of guidance consisting of statements of basic requirements for the practice of internal audit and interpretations that clarify terms or concepts within those statements. The Standards were last updated on 1 January 2017.
The structure of the Standards is divided between attribute and performance standards:
- Attribute standards address the attributes of organisations and individuals performing internal auditing.
- Performance standards describe the nature of internal auditing and provide quality criteria against which the performance of these services can be measured.
Recommended guidance
The IPPF also includes guidance to help internal auditors implement the Standards and apply best practice to all internal audit work. This forms the 'recommended' element of the framework.
Two kinds of guidance are produced:
1. Implementation guidance
Implementation guides help internal auditors apply the Standards. They collectively address internal auditing's approach, methodologies, and consideration, but do not detail processes or procedures.
2. Supplemental guidance
Supplemental guidance describes processes and procedures in detail as well as sector specific issues and topical areas. These guides will help you develop the tools, techniques and programmes you need with a step-by-step approach. Supplemental guidance will also help you to determine what the deliverables are.
Position Papers
Position Papers set out the position of IIA Global in relation to a number of topics, including Fraud and Internal Audit and Internal Audit's role in Corporate Governance.








